CSS in React
CSS in React
- CSS in HTML
- React Generates HTML
- CSS in React
- React Elements vs HTML Elements
- (Not) Thinking in React
- To-Do List Example
- Learn More
Now you know how to build a React app using stateful components. So far, all of the example apps used unstyled HTML. This tutorial walks through using CSS in React so you can style your React apps.
CSS in HTML
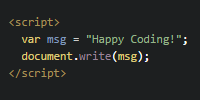
Before we talk about CSS in React, think about how CSS works in plain old HTML. You can style elements directly, or you can use classes or IDs:
See the Pen by Happy Coding (@KevinWorkman) on CodePen.
If you’re not familiar with CSS, you can learn more here:
React Generates HTML
To understand CSS in React, keep in mind that React’s end result is plain old HTML (and JavaScript).
For example, try inspecting the resulting HTML of this React code:
See the Pen by Happy Coding (@KevinWorkman) on CodePen.
That React code generates this HTML content:
<div id="root">
<div>
<h1>Things</h1>
<ul>
<li>Thing 1</li>
<li>Thing 2</li>
<li>Thing 3</li>
<li>Thing 4</li>
<li>Thing 5</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
Although the React code contains a Thing component, the resulting HTML only contains HTML tags like <div>, <h1>, <ul>, and <li>.
CSS in React
Now you know that React generates HTML, and you can use CSS from HTML. With that in mind, using CSS in React is all about getting React to include CSS classes and styling in the resulting HTML.
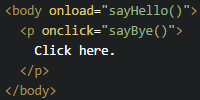
For the most part, CSS in React works exactly like it works in HTML. You can include a stylesheet, a <style> element, or inline styles in your HTML to style your elements:
See the Pen by Happy Coding (@KevinWorkman) on CodePen.
The only exception is that React does not use the class attribute to assign a CSS class to an attribute. That’s because React is JavaScript, and the class keyword is reserved in JavaScript.
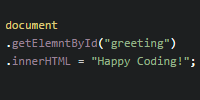
Instead, use the className attribute:
See the Pen by Happy Coding (@KevinWorkman) on CodePen.
This example contains a couple interesting parts.
First, this section of code creates an <h1> element with a className of heading:
<h1 className="heading">
Things
</h1>
Then, the Thing component renders an <li> element, and gives the <li> a className based on its isEven property.
class Thing extends React.Component {
render() {
return <li className={this.props.isEven ? "even" : "odd"}>
Thing {this.props.index}
</li>;
}
}
Finally, the CSS styles the elements, IDs, and classes. This works exactly the same as it works in regular HTML, because that’s what React generates!
<style>
#root {
border: thin solid black;
width: 500px;
margin: auto;
}
.heading {
text-align: center;
font-style: italic;
}
li {
list-style: none;
width: 200px;
padding: 10px;
}
.even {
background: cyan;
}
.odd {
background: purple;
color: white;
}
</style>
React Elements vs HTML Elements
When you’re writing React, you’re probably writing JSX. JSX syntax looks like HTML inside of JavaScript, but it’s really plain old JavaScript behind the scenes.
You can use the Babel browser translator to see the JavaScript that’s generated from a snippet of JSX. Try converting this JSX to JavaScript:
<h1 className="heading">Things</h1>
That JSX is converted to this JavaScript:
React.createElement("h1", {className: "heading"}, "Things");
This JavaScript calls the React.createElement() function, tells it to represent an h1 tag, passes it an object containing the className attribute, and gives it a content argument of "Things".
To understand why you have to use className instead of class, try this instead:
<h1 class="heading">Things</h1>
If you try to use the class attribute in your JSX, you’ll get this error:
Warning: Invalid DOM property `class`. Did you mean `className`?
That’s because the above JSX generates this JavaScript:
React.createElement("h1", {class: "heading"}, "Things");
This JavaScript is invalid, because class can’t be a variable name. That’s why JSX uses className: because it’s not HTML, it’s JavaScript!
If using className instead of class is still confusing, here’s how I think about it: JSX creates a React element, which is a JavaScript object that contains a className variable. React then converts that React element into an HTML element containing a class attribute, and the HTML element is added to the DOM.
(Not) Thinking in React
In most of my other React tutorials, I’ve talked about how React makes more sense if you “think in React”. React has its own opinions about how code and data should be organized, and understanding those opinions can help you understand why React works the way it does.
However, I think understanding CSS in React is more about thinking in HTML, not in React. React itself doesn’t care about CSS at all! It’s all about the final generated HTML, which is what the CSS ends up styling.
So if you find yourself asking a question about using CSS in React:
- How do I turn a button red in React?
- In React, how do I italicize every other element?
- How to style text in React?
You should instead ask yourself the same question, but without React at all:
- How do I turn a button red in HTML?
- In HTML, how do I italicize every other element?
- How to style text in HTML?
Research that question, and then think about how you’d generate that HTML using React.
To-Do List Example
Here’s our handy dandy to-do list example, with some beautiful CSS styling:
See the Pen by Happy Coding (@KevinWorkman) on CodePen.