Unsanitized User Input
Previous:
Unsanitized User Input
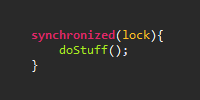
This example uses an HTML form to create a POST request containing the user’s name.
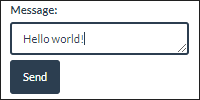
index.html contains an HTML form:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Enter some input:</h1>
<form action="/user-input-unsanitized/form" method="POST">
<input type="text" name="data" value="<h1>oh no</h1>">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
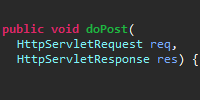
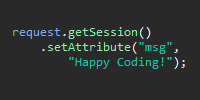
FormServlet.java handles the POST request by outputting the user’s input directly to the response:
package io.happycoding.servlets;
import java.io.IOException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/form")
public class FormServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException {
String data = request.getParameter("data");
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.getWriter().println("You entered: " + data);
}
}
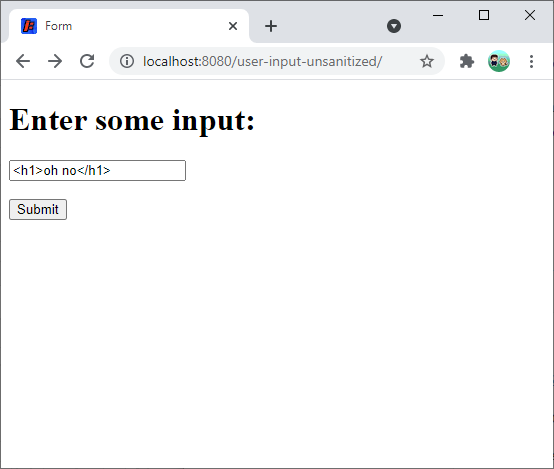
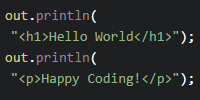
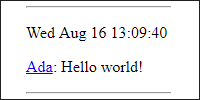
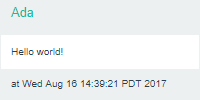
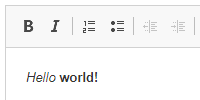
Because the servlet does not sanitize the data, the HTML is rendered in the output:
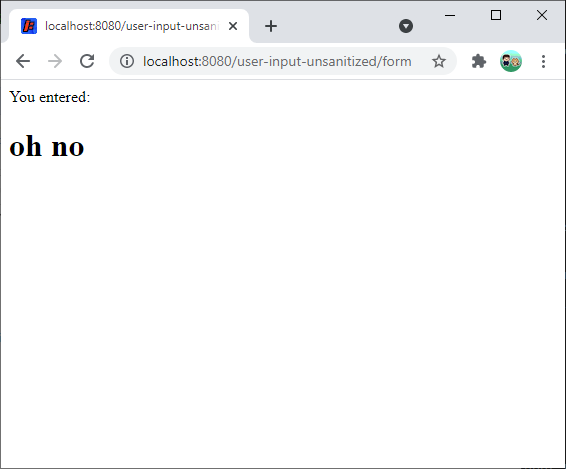
See the server libraries tutorial and the sanitizing user input tutorial for more information about why this is bad, and what to do about it.
Previous: